Scientific topics Critical minerals at Geoscience Australia
Page last updated:26 March 2025
Geoscience Australia supports the objectives of Australia’s Critical Minerals Strategy 2023–2030 to grow our critical minerals sector, expand downstream processing, and help meet future global demand. We support the Critical Minerals Office to help grow Australia's critical minerals sector and position Australia globally as a secure, reliable, and ethical supplier of critical minerals.
Our critical minerals activities include:
- Technical advice to government
- Scientific research including pre-competitive data acquisition
- Data enabling services and decision-support tools
- International and national collaborations
- Publications
- Public communication
- Investment attraction
These activities align with Geoscience Australia’s priority stream of Building Australia’s resources wealth under Strategy 2028, in particular the Resourcing Australia’s Prosperity initiative, which aims to accelerate the discovery of critical minerals and other resources to support Australia’s net zero transition and enable responsible management of all resources.
What is a critical mineral?
A critical mineral is a metallic or non-metallic element that has two characteristics:
- It is essential for the functioning of our modern technologies, economies or national security and
- There is a risk that its supply chains could be disrupted.
Critical minerals are used to manufacture advanced technologies including mobile phones, computers, fibre-optic cables, semi-conductors, banknotes, and defence, aerospace and medical applications. Many critical minerals are used in low-emission technologies such as electric vehicles, wind turbines, solar panels, and rechargeable batteries. While some are also crucial for common products such as stainless steel and electronics.
Risks to critical mineral supply chains can come about when mineral production or processing is dominated by individual countries or companies that could limit availability. Other risks include market immaturity, political decisions, social unrest, natural disasters, mine accidents, geological scarcity, pandemics, and war.
Overview of Critical Minerals
A critical mineral is a metallic or non-metallic element that is essential for modern technologies, economies, national security, and has a supply chain at risk of disruption. Individual countries develop their own lists of critical minerals based on the relative importance of particular minerals to their industrial needs and strategic assessment of supply risks. In addition, assessments of mineral criticality reflect market and political conditions at a particular point in time and are subject to change.
As of 20 February 2024, the Australian Government considers 31 resource commodities to be critical minerals. These have been selected by assessing Australia’s geological endowment and potential with global technology needs, particularly those of partner countries such as the United States, European Union, India, Japan, South Korea and the United Kingdom. Australia’s 31 critical minerals are listed in the table below with more information here or in the Critical Minerals Strategy 2023–2030.
Australia's critical minerals list, resources and production with global comparisons.
| Critical mineral | On US list1 | On EU list2 | On India list3 | On Japan list4 | On ROK list5 | On UK list6 | Australian geological potential7 | Australian economic demonstrated resources (2022)8 | Australian production (2022)9 | World resources (2022)10 | Global production (2022)11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-purity Alumina | No | No | No | No | No | No | High | HPA ore: 16,700 kt | 0 | No data | No data |
| Antimony | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Moderate | 139.4 kt | 2.3 kt | 1,800 kt | 110 kt |
| Arsenic | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | Moderate | No data | No data | No data | 61 kt |
| Beryllium | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Moderate | No data | No data | No data | 280 t |
| Bismuth | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Moderate | No data | No data | No data | 20 kt |
| Chromium | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate | 0 | 0 | 560,000 kt | 41,000 kt |
| Cobalt | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | 1,742 kt | 5.8 kt | 8,480 kt | 185 kt |
| Fluorine12 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Moderate | 343 kt | 0 | 126,000 kt | 4,000 kt |
| Gallium | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | No data | No data | No data | 550 t |
| Germanium | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | High | No data | No data | No data | No data |
| Graphite13 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Moderate | 8,500 kt | 0 | 332,000 kt | 1,300 kt |
| Hafnium | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Moderate | 14.5 kt | No data | No data | No data |
| Indium | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Moderate | No data | No data | No data | 900 t |
| Lithium | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | 7,046 kt | 75 kt | 27,000 kt | 143 kt |
| Magnesium | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | Magnesite: 284,000 kt | Magnesite: 500 kt | Magnesite: 6,800,000 kt | Magnesite: 25,000 kt |
| Manganese | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | High | Manganese ore: 496,000 kt | Manganese ore: 4,500 kt | Manganese content: 1,716,000 kt | Manganese content: 18,700 kt |
| Molybdenum | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Moderate | 687 kt | 0.28 kt | 12,200 kt | 250 kt |
| Nickel | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | High | 24.1 Mt | 0.15 Mt | 104 Mt | 3.3 Mt |
| Niobium | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unknown (interpreted moderate)14 | 216 kt | No data | Over 17,000 kt | 79 kt |
| Platinum-group elements15 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Moderate | 359.3 t | 0.492 t | 71,269 t | 400 t |
| Rare-earth elements16 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | 5,700 kt | 16 kt | 127,000 kt | 300 kt |
| Rhenium | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Unknown (interpreted moderate) | 157 t | No data | No data | 58 t |
| Scandium | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | High | 36.65 kt | 0 | No data | No data |
| Selenium | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Unknown (interpreted moderate) | No data | No data | 81 kt | 3.2 kt |
| Silicon | No | Yes17 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | No data | No data | No data | 8.8 kt |
| Tantalum | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | 110 kt | 0.1 kt | No data | 2 kt |
| Tellurium | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Unknown (interpreted moderate) | No data | No data | 32 kt | 0.64 kt |
| Titanium | Yes | Yes18 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | High |
Ilmenite: 303,300 kt Rutile: 39,000 kt |
Ilmenite: 700 kt Rutile: 200 kt |
Ilmenite: 1,106,600 kt Rutile: 55,900 kt |
Ilmenite: 14,900 kt Rutile: 600 kt |
| Tungsten | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | 568 kt | 0.23 kt | 3,800 kt | 84 kt |
| Vanadium | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | High | 8,510 kt | 0 | 26,700 kt | 100 kt |
| Zirconium | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | High | Zircon: 88,300 kt | Zircon: 500 kt | Zircon: 115,300 kt | Zircon: 2,200 kt |
- J Burton, U.S. Geological Survey Releases 2022 List of Critical Minerals , United States Geological Survey (USGS), U.S. Department of the Interior, Federal Government of the United States, 2022, accessed 6 December 2023.
- Fifth list 2023 of Critical Raw Materials for the EU, European Commission, 2023, accessed 6 December 2023.
- Critical Minerals for India , Ministry of Mines, Government of India, 2023, accessed 6 December 2023.
- Japan Oil, Gas and Metals National Corporation (JOGMEC), International Resource Strategy National Stockpiling System, International Energy Agency (IEA), 2020, accessed 6 December 2023.
- Opportunities in Korea for Australian Critical Minerals, Australian Trade and Investment Commission, 2023, accessed 6 December 2023.
- Resilience for the Future: The UK's Critical Minerals Strategy, United Kingdom Department for Business & Trade and Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy, 2023, accessed 6 December 2023.
- Geoscience Australia, Overview of Critical Minerals , Geoscience Australia, Australian Government, accessed 6 December 2023, and additional correspondence.
- Geoscience Australia, Overview of Critical Minerals, Geoscience Australia, Australian Government, accessed 6 December 2023.
- Geoscience Australia, Overview of Critical Minerals, Geoscience Australia, Australian Government, accessed 6 December 2023
- Geoscience Australia, Australia's Identified Mineral Resources 2023 , Geoscience Australia, Australian Government, accessed 6 December 2023.
- Geoscience Australia, Australia's Identified Mineral Resources 2023 , Geoscience Australia, Australian Government, accessed 6 December 2023.
- The United States and the European Union identify fluorspar as a critical mineral.
- The European Union identifies natural graphite as a critical raw material and Japan identifies carbon (which forms graphite) as a critical mineral.
- Unknown geological potential owing to lack of data. Interpretation is based on knowledge of Australia's geology, known mineral associations and historical information.
- The platinum group elements include ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium, and platinum. Several partner lists separately identify the platinum group elements and/or only identify certain platinum group elements as critical minerals.
- The rare earth elements include yttrium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, and lutetium. Several partner lists separately identify the rare earth elements and/or only identify certain rare earth elements as critical minerals.
- The European Union identifies silicon metal as a critical raw material.
- The European Union identifies titanium metal as a critical raw material.
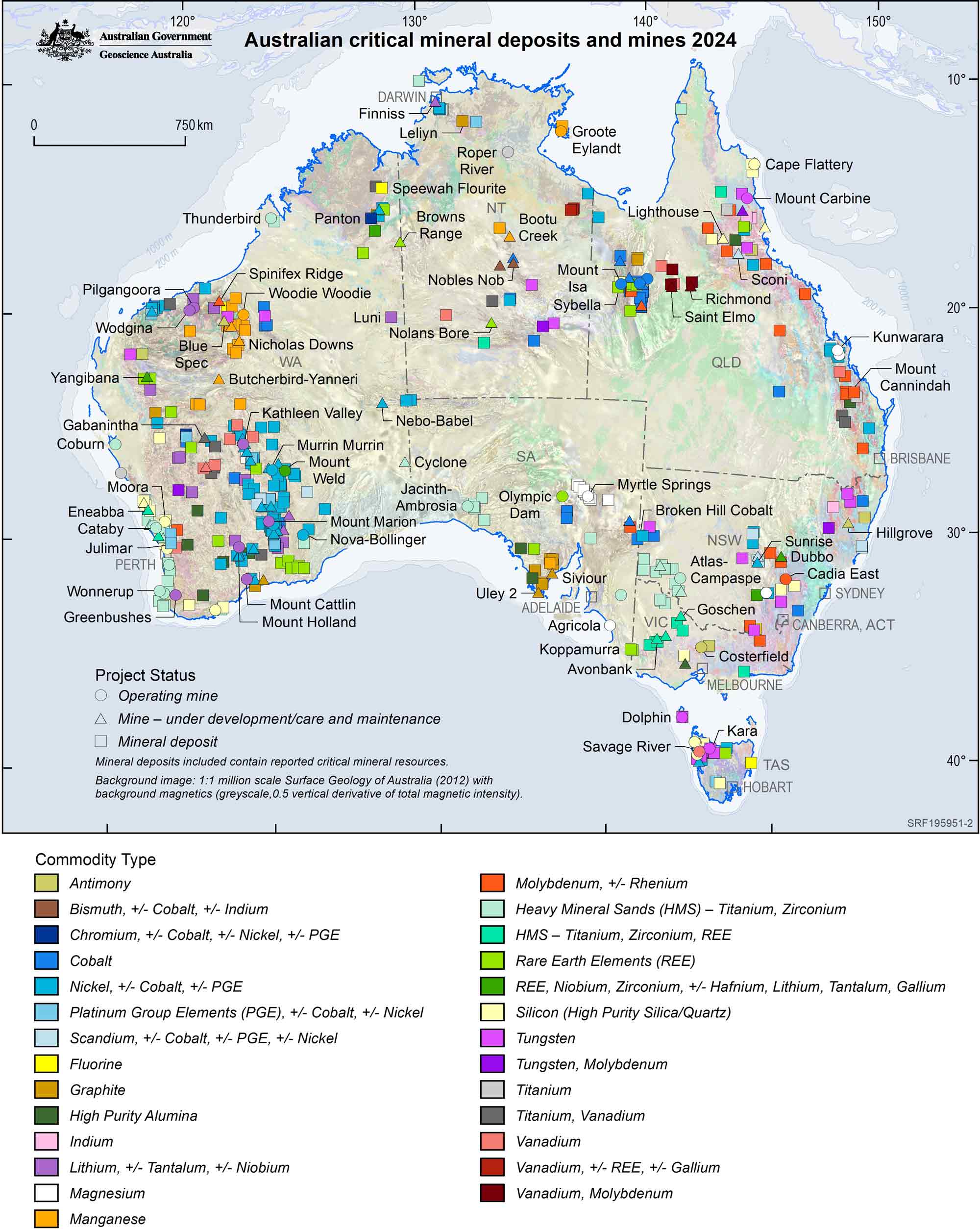
Australia’s critical minerals sector is constantly growing in response to the increasing global need for a secure supply of these vital and strategic minerals. Australia’s Identified Mineral Resources 2024 shows that, in 2023, Australia retained its position as the world’s top lithium producer (49%) and was also a top five producer for cobalt (2%), manganese ore (9%), rare earths (8%), rutile (35%), tantalum (6%), and zircon (24%). As well as being a global leader in the supply of critical minerals, many more deposits have been discovered or are under development, as seen in the map below.
The Australian resources industry has responded to increased demand for critical minerals with additional exploration and resource definition. There was significant growth in the economic inventories of 13 critical minerals and strategic materials. Economic inventories increased for platinum group elements (up 30%), graphite (up 27%), lithium (up 20%), niobium and vanadium (both up 18%), manganese ore (up 16%), high-purity alumina (up 14%), molybdenum, rare earths and tantalum (all up 10%), rutile (up 6%) and bauxite (up 5%). In addition, new economic resources (748 kt) were recorded for chromium. Information regarding developing and advanced-stage critical minerals projects in Australia, can be found in the Australian Critical Minerals Prospectus 2023.
Click for further information about each critical mineral.
Resourcing Australia’s Prosperity
Resourcing Australia’s Prosperity is the Australian Government’s 35-year, $3.4 billion precompetitive geoscience initiative, led by Geoscience Australia, to accelerate the discovery of critical minerals and other resources, to support Australia’s net zero transition and enable responsible management of all resources.
The landmark Resourcing Australia’s Prosperity initiative (2024-59) will play a key role in unlocking new opportunities to support a thriving and resilient national economy and a Future Made in Australia.
It will use innovative data, research and analysis to assess national potential for a broad range of the resources critical to the net zero transition, supporting a strong resource sector. This initiative focuses on mapping our potential for critical minerals and strategic materials, hydrogen and carbon storage, and offshore renewable energy. It will also map the groundwater systems that support the development of our natural resources, contribute to our water and food security, and bolster our climate resilience.
Resourcing Australia’s Prosperity will drive economic growth and create jobs in the global shift to a net zero economy. By partnering with state and territory governments and our research partners, this initiative also lays the groundwork for a prosperous, competitive and sustainable future.
Exploring for the Future
The Australian Government’s $225 million Exploring for the Future program (2016-24), led by Geoscience Australia, committed to supporting a strong economy, resilient society and sustainable environment for the benefit of Australians.
At its heart, the program was about contributing to a sustainable, long-term future for Australia through an improved understanding of the nation’s mineral and energy potential and groundwater resources.
By gathering and analysing geological and geophysical data and making the results publicly available, the program supported regional development and informed decision making across Australia, resulting in jobs and growth.
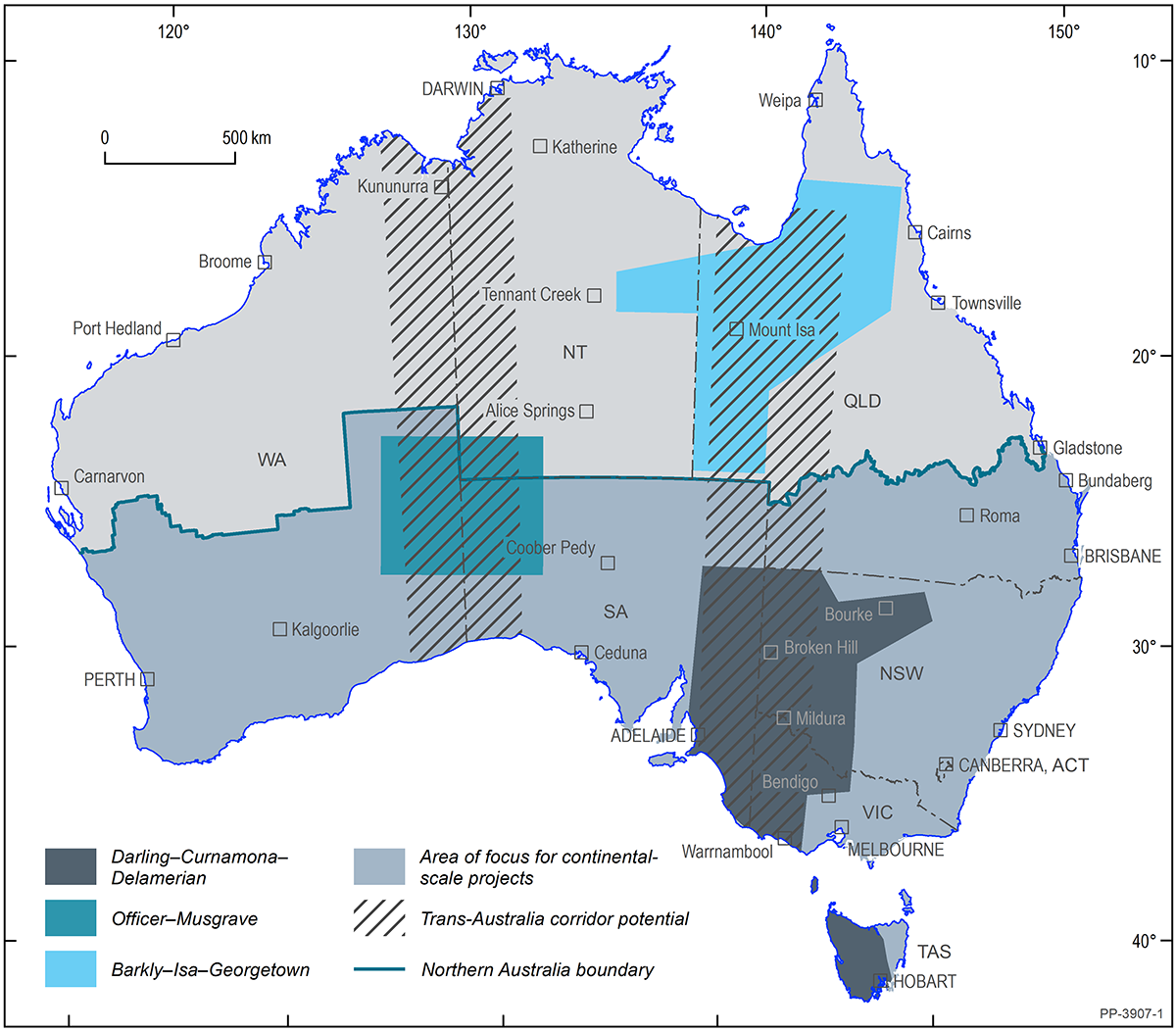
The 2020–2024 program focused on eight interrelated projects, united in growing our understanding of subsurface geology. Three of these projects had an application to critical minerals: Australia’s Resources FrameworkAustralia’s as a continental-scale project; Darling-Curnamona-Delamerian as a regional-scale deep-dive project across western New South Wales and Victoria, eastern South Australia, and northwest Tasmania; and Barkly-Isa-Georgetown as a regional-scale deep-dive project between Tennant Creek in the Northern Territory, through to Mount Isa and Georgetown in Queensland.
Australian Critical Minerals Research and Development Hub
The (the R&D Hub) is hosted by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) and brings together expertise from leading Federal science agencies: the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) and Geoscience Australia.
The R&D Hub will work with industry to address technical challenges and drive collaborative research across the critical minerals value chain needed to support clean energy and Australia’s net zero policy agenda.
The top priorities of the R&D Hub are to:
- scale-up and commercialise critical minerals research and development – including priority research projects on supply chains of strategic significance
- help coordinate, guide and prioritise critical minerals research and development efforts across Australia
- connect critical minerals projects to the technical and research expertise they need
- support strategic international critical minerals collaboration and science diplomacy.
Find out more about Geoscience Australia’s projects that are funded through the Australian Critical Minerals R&D Hub.
Critical Minerals Mapping Initiative
The importance of critical minerals and the need to expand and diversify critical mineral supply chains has been endorsed by the federal governments of Australia, Canada, and the United States. The geoscience organisations of Geoscience Australia, the Geological Survey of Canada and the United States Geological Survey have created the Critical Minerals Mapping Initiative (CMMI) to build a diversified critical minerals industry in all three countries. The aim of this collaboration is to utilize our combined geological expertise to address global natural resource vulnerabilities whilst also highlighting emerging opportunities in the resource sector and promoting critical mineral discovery in Australia, Canada and the USA.
CMMI is developing a better understanding of:
- Known critical mineral resources.
- Geologic controls on critical mineral distribution for deposits currently producing by-products.
- Identification of new sources of supply through critical mineral potential mapping and quantitative mineral assessments.
As part of the initiative, CMMI has combined the mineral resources information held by the three geoscience organisations into a singular dataset to create the world’s largest compilation of Critical Minerals in Ores. This data is available through the CMMI Portal, a free interactive mapping tool designed to display critical minerals information on a global scale. It includes over 25,000 mineral samples provided by 60 countries, from both historical and modern mining operations. New data and publications from the collaboration will be added to the portal as they become available.
Investors
Australia has a rich and diverse mineral endowment and long history of discovering and responsibly developing high-quality mineral resources. This, combined with vast tracts of largely under-explored and highly prospective areas, makes Australia an ideal place for investment in mineral exploration.
In addition, Australia’s adherence to the rule of law creates an investment environment of low political and sovereign risk. Investors can have confidence in consistent and transparent management of economic settings such as labour, taxes, royalties, health and safety, skilled migration, foreign investment and environmental protection as they operate in a strong and well-established resources industry. This robust framework combined with Australia’s enormous resource wealth, huge potential for new discoveries and well-coordinated government support for exploration and resource development creates a competitive advantage for investors in Australia’s mineral resources sector.
Geoscience Australia:
- Supports the objectives of Australia’s Critical Minerals Strategy 2023–2030 to grow our critical minerals sector, expand downstream processing and help meet future global demand.
- Supports the Critical Minerals Office to help grow Australia's critical minerals sector and position Australia globally as a secure, reliable and ethical supplier of critical minerals.
- Works with Austrade to promote investment opportunities in Australian critical minerals projects to investors. These government agencies, publications and resources help investors find opportunities and navigate approval requirements to invest in Australia.
Read more:
- Austrade
- Australia Minerals
- Critical Minerals Strategy 2023–2030
- Australian Critical Minerals Prospectus 2023
- Australian Energy and Mineral Resources Investor Guide 2020
- Foreign Investment Review Board
- Major Projects Facilitation Agency
- Northern Australia Infrastructure Facility
- Export Finance Australia
Publications
Science and technical information
- Australia’s Identified Mineral Resources (2024)
- Australian Mineral Exploration Review (2023)
- Deposit Classification Scheme for the Critical Minerals Mapping Initiative Global Geochemical Database (2021)
- Geological Surveys United to Improve Critical Mineral Security (2021)
- International database on the abundance of critical minerals in ore: Relevance to research and development of critical mineral resources (2021)
- Outlook for Selected Critical Minerals Australia (2021)
- Critical Energy Minerals Roadmap CSIRO (2021)
- International Geoscience Collaboration to Support Critical Mineral Discovery (2020)
- Critical Minerals in Australia: A Review of Opportunities and Research (2019)
- Critical commodities in Australia – an assessment of extraction potential from ores (2017)
- Critical Commodities for a High-tech world (2013)
- Australian Resource Reviews
Maps
Policy
- The 2023-2030 Critical Minerals Strategy outlines priorities for the development of Australia’s critical minerals sector to ensure that it can seize the opportunities of the net zero transformation
- The Australian government is committed to developing the country’s first National Battery Strategy to articulate a clear pathway for integrated, end-to-end onshore battery minerals supply chains
- The Australian government has committed $15 billion to establish the National Reconstruction Fund to provide finance for projects that diversify and transform Australia’s industry and economy.
Presentations and videos
Geoscience Australia has also produced a series of presentations on critical minerals, many of which can be found on our YouTube page.
Relevant presentations include: