Rocks
The term rock is used to describe a naturally occurring solid aggregate of one or more minerals. The term mineral is used to describe a naturally occurring substance with a reasonably fixed chemical composition and crystal structure.
Videos
Sugar shake: erosion experiment (primary)
This video introduces the concepts of weathering and erosion by investigating why river pebbles are often rounded. Viewers can undertake an activity which demonstrates the process of erosion using sugar cubes.
The Geology of Minecraft
How do some of the rocks in Minecraft form and behave in real life? This short video discusses bedrock, obsidian and redstone using real rock samples and references to the game.
Rocks from volcanoes
This short video introduces rocks from volcanoes and their features using some of the samples in the Geoscience Australia Education Centre.
Earth Science 101 – The Rock Cycle
Introductory video on the rock cycle - suitable for high school students and adults (12 minutes).
Virtual Exhibits

Learn about the many minerals, both common and rare, that are essential for modern technology and renewable energy

An introduction to minerals and their properties such as hardness and streak

View the valuable gem and mineral specimens that are not on public display

Broken Hill: One of the world’s largest lead-zinc-silver deposits
Learn about one of the greatest ore deposits in the world and view spectacular and rare mineral specimens

A showcase of radioactive specimens from the National Mineral Collection

Learn about the national gemstone, where it is found and what types there are

Rocks that get excited… under ultraviolet light!
Teacher Guides and Resources

Weathering, erosion, landforms and regolith - Teacher notes and student activities
This booklet focuses on the processes of weathering and erosion, and includes case studies on Australian landforms such as Uluru, the Warrumbungles and the Twelve Apostles.

Exploring Minerals and Crystals - Teacher notes and student activities
Explore important concepts about minerals and crystals using this comprehensive resource. Includes sections on identifying minerals, significant minerals and gem resources in Australia and the uses of crystals. Contains student activities and answers.

Geological TimeWalk - A Short Guide
This booklet describes major geological, climatic and biological events that have occurred over time. Geological events include continental drift, the break-up and amalgamation of continental land masses, mountain building and major volcanic eruptions. Climate changes include the occurrence of ice ages and biological events include the evolution of major groups of organisms.

Discovering geological maps (legacy product)
Poster describing each of the elements on a geological map including symbols, grid references, cross-section, scale, geological reliability diagram and the geological time scale.

Geology of Minecraft & Geology of Minecraft 2
Posters comparing the concepts in the computer game Minecraft with science/geology. Aimed at school children, for display in classrooms.

Our Changing Earth - Rock Cycle
A simple rock cycle poster showing the formation and features of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks.

Theoretical geological cross section from the ocean through a mountain range to inland plains.
Student Activities

Explore the concepts of weathering and erosion by investigating why river pebbles are often rounded.
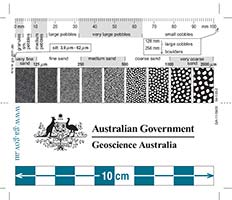
This card is useful for analysis of sediments – size, roundness, sorting.
Further information

Shaping a Nation: A geology of Australia book
Exploring the geology, resources and landscapes of Australia, this comprehensive book reveals how these have helped to shape this nation's society, environment and wealth.

Web pages with links to Australian minerals and energy facts.
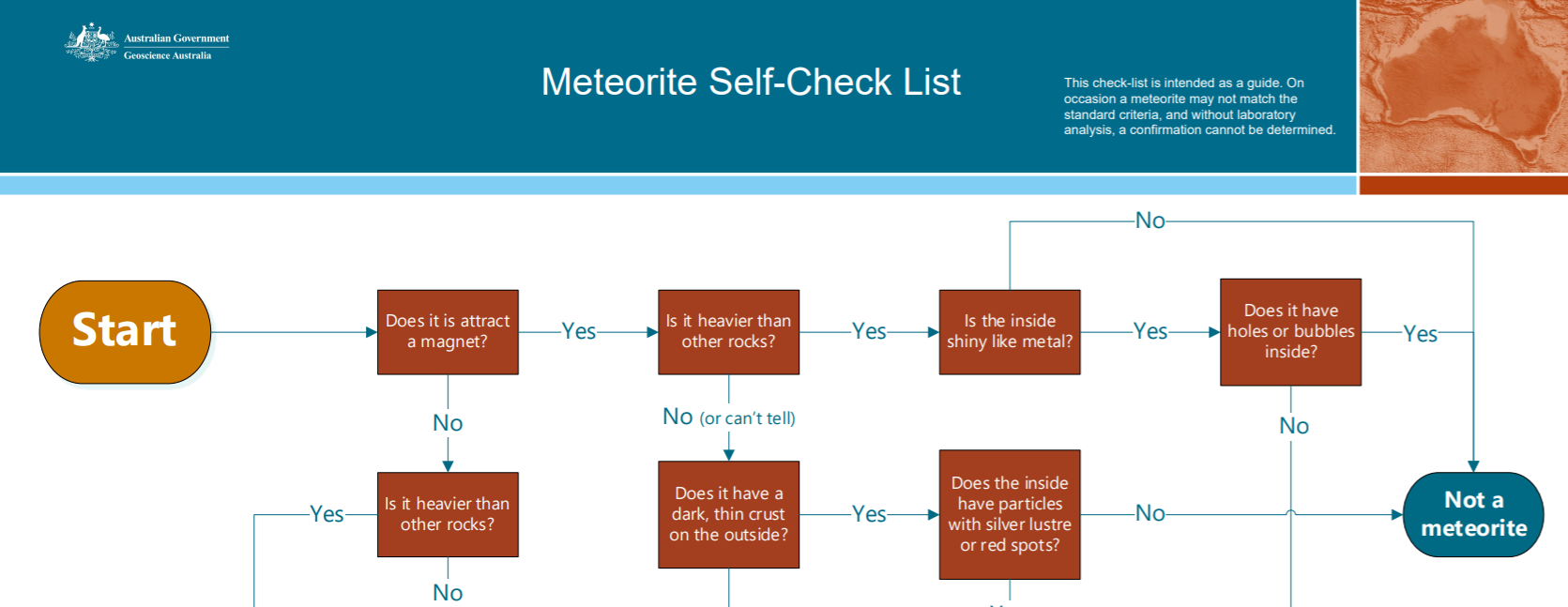
Meteorite identification self-check list
A self-checker to help identify if you have a meteorite.

Web pages about minerals found and mined in Australia.
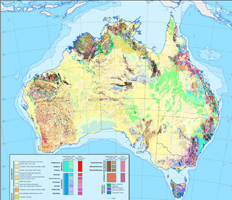
JPG or PDF download of surface geology map of Australia, A3 size.
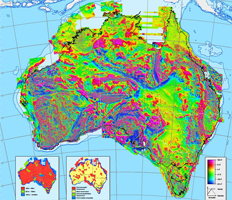
Magnetic anomaly map of Australia
A3 PDF magnetic intensity map of Australia.
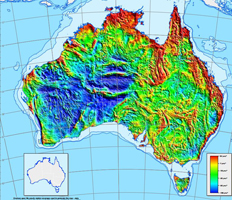
Gravity anomaly map of Australia
PDF download of the gravity anomaly map of the Australian region.
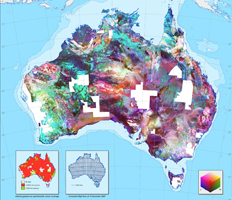
PDF A3 and A0 version of the radiometric map of Australia.

Rock and Fossil self-guided tour of the Australian Capital Territory
To celebrate the establishment of the Australian Capital Territory (ACT) fossil emblem in 2020 this self-guided tour was developed to guide visitors to a number of interesting geological locations around metropolitan Canberra and surrounds.
Australian Curriculum links
Year 4
Science > Science Understanding > Earth and Space Science > Earth’s surface changes over time as a result of natural processes and human activity (ACSSU075)
Year 7
Science > Science Understanding > Earth and Space Science > Some of Earth’s resources are renewable, including water that cycles through the environment, but others are non-renewable (ACSSU116)
Year 8
Science > Science Understanding > Earth and Space Science > Sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic rocks contain minerals and are formed by processes that occur within Earth over a variety of timescales (ACSSU153)
Senior Secondary
Earth and Environmental Science > Unit 1: Introduction to Earth systems > Rocks are composed of characteristic assemblages of mineral crystals or grains that are formed through igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic processes, as part of the rock cycle (ACSES019)
Earth and Environmental Science > Unit 3: Living on Earth – extracting, using and managing Earth resources > Non-renewable mineral and energy resources are formed over geological time scales so are not readily replenished (ACSES071) > The location of non-renewable mineral and energy resources, including fossil fuels, iron ore and gold, is related to their geological setting (for example, sedimentary basins, igneous terrains) (ACSES072)





